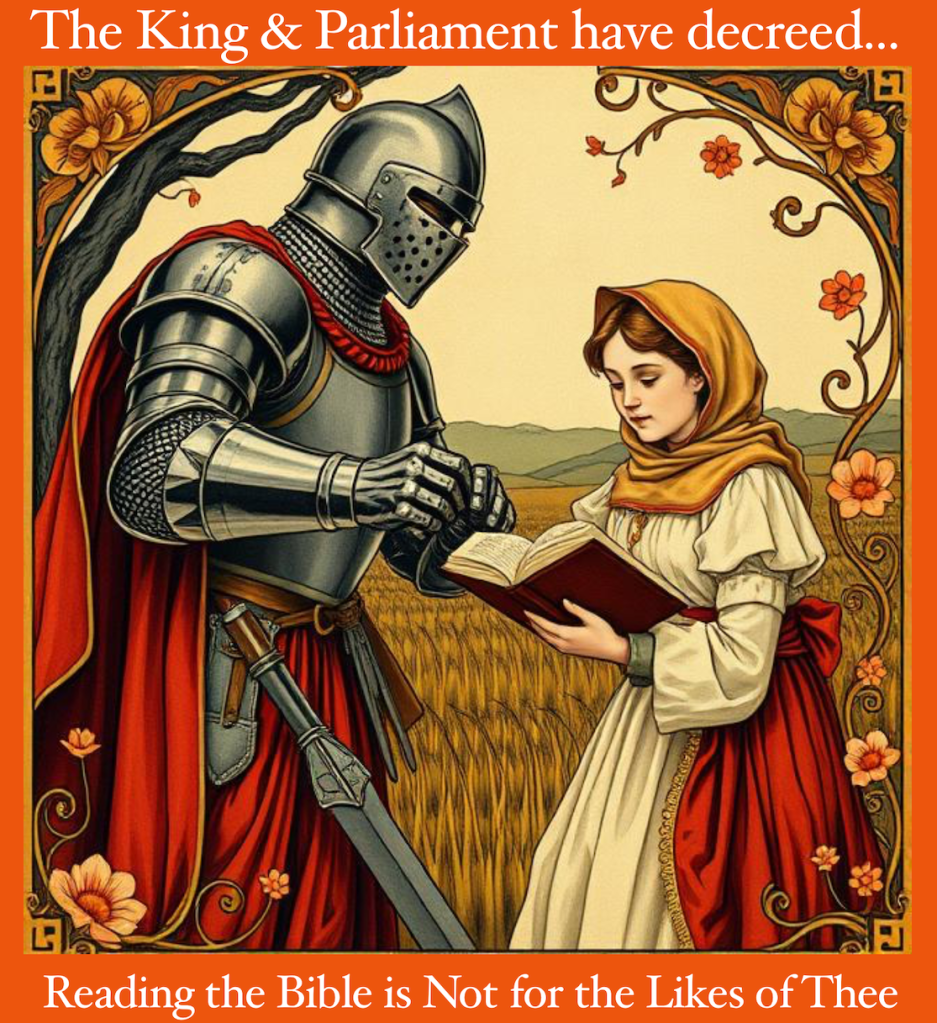
How would you respond if the government prohibited you from reading the Holy Scriptures? That was the situation in Great Britain when the Parliament passed the ironically named “Act for the Advancement of True Religion.”
Nearly five centuries ago, on May 12, 1543, Britain’s enlightened politicians and bishops determined that people of the “lower sort” needed to be protected from reading and interpreting the Bible themselves.
Just sixty-one years later, King James VI/I would commission the translation of the Authorized Version, making God’s Word more accessible to all who could read English. William Tyndale (c. 1494 – 1536) had actually translated a fair portion of the Scriptures a decade prior to Parliament’s restrictive law. For this, and similar “Protestant” sins, Tyndale was strangled and burned at the stake in Belgium.
Even the so-called Great Bible had been authorized by Henry VIII in 1539. The approval decreed “one book of the bible of the largest volume in English, and the same set up in some convenient place within the said church that ye have care of, whereas your parishioners may most commodiously resort to the same and read it [emphasis mine].”
Nevertheless, not all of the powers that be apparently agreed with making the text of the Bible accessible to the common folk. We will consider this category of “inadequates” momentarily.
First let’s consider the distaste expressed by some for any modern translation of the Scriptures. (If you’ve ever attended a Bible study group you have probably encountered at least one person who insists on using the true KJV, despite the archaic language.
C.S. Lewis addressed this reticence for clear translations in an essay entitled “Christian Apologetics.” It was originally presented to Anglican priests and youth leaders in 1945.
“Do we not already possess,” [some will say] “in the Authorised Version the most beautiful rendering which any language can boast?” Some people whom I have met go even further and feel that a modern translation is not only unnecessary but even offensive.
They cannot bear to see the time-honoured words altered; it seems to them irreverent. There are several answers to such people. In the first place the kind of objection which they feel to a new translation is very like the objection which was once felt to any English translation at all.
Dozens of sincerely pious people in the sixteenth century shuddered at the idea of turning the time-honoured Latin of the Vulgate into our common and (as they thought) ‘barbarous’ English. A sacred truth seemed to them to have lost its sanctity when it was stripped of the polysyllabic Latin, long heard at Mass and at Hours, and put into . . . language steeped in all the commonplace associations of the nursery, the inn, the stable, and the street.
The Biblically Unworthy
So, who were these “lower sort” of individuals deemed unsuited for reading the Scriptures already translated into their native tongue? Well, they included “women, artificers, apprentices, journeymen, serving-men of the rank of yeoman and under, husbandmen and laborers.” Women of the gentry class were allowed an exception, being able to read the Scriptures, but only in private.
Fortunately, the law was short-lived. Henry’s son, Edward VI/I would have it repealed in the Treason Act of 1547. (Of course, this goodwill did not prevent Edward from condemning the translations of the aforementioned martyr, William Tyndale.)
Who Should Read the Bible?
The short answer is “everyone.” Yet the fact exists that some individuals are susceptible to confusion – or even to intentional twisting of the clear meaning of God’s Word. So, while the Scriptures should be accessible to all, it is wise to guide children and the easily-confused in their studies. After all, what we all desire is honest understanding and enlightenment.
This direct access is one reason Martin Luther, William Tyndale and others labored so tirelessly to translate the Bible into the vernacular. Cheerfully, “believers no longer had to read Latin [or Greek, Hebrew or Aramaic] to understand the word of God.”
As for those who would directly attempt to distort God’s inspired words, a clear example is found in the New World version paraphrase invented by Jehovah’s Witnesses. Another example, which I have discussed in the past, is the distorted abomination created by the Chinese Communist Party.
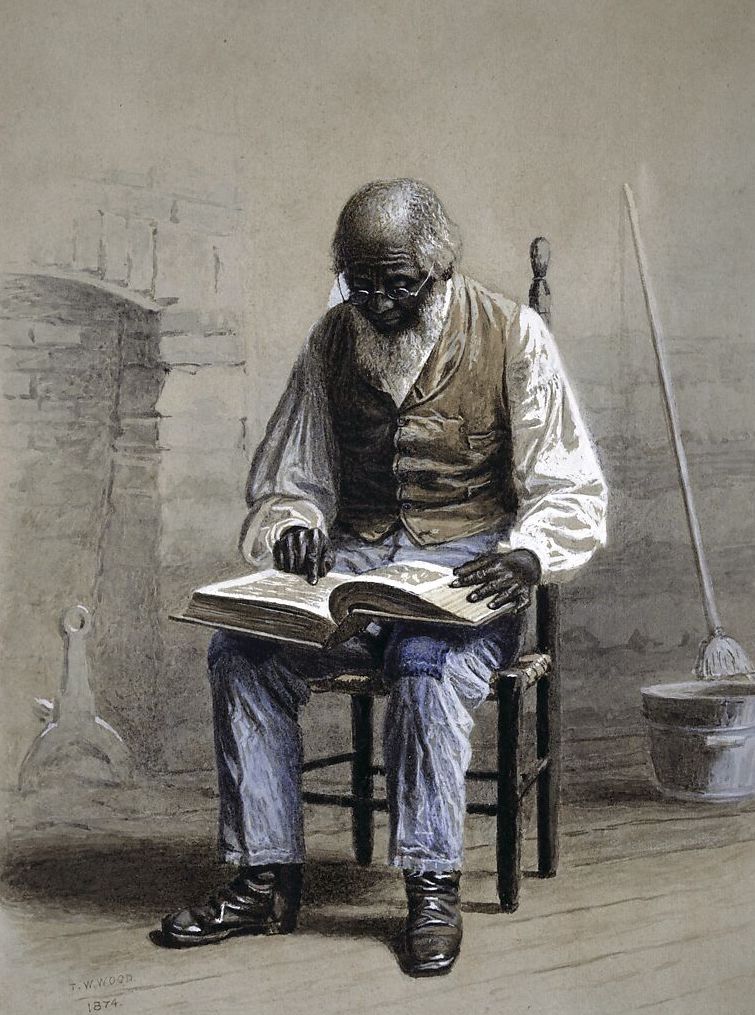
There are also “abbreviated” versions of the Bible, which contain properly translated passages, but leave out passages that challenge preconceived positions. This would include Thomas Jefferson’s cut and paste Bible and an edition of the Scriptures developed for teaching slaves to read.
If you are interested in receiving daily notes about Christian history such as the one which prompted this post, visit the Christian History Institute.