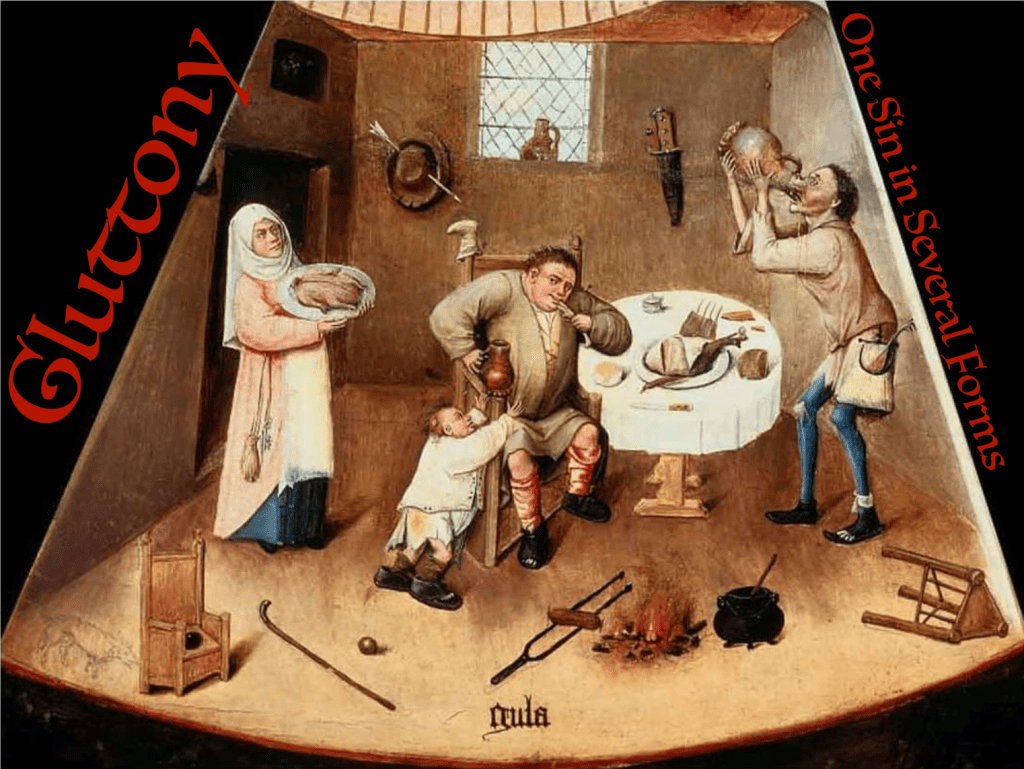
Gluttony. If you were guilty of committing this sin, would you admit it? How, in fact, can we determine whether we (much less someone else) is a glutton?
And, even if we do fit the description of a glutton, is it all that bad? I mean, it’s not like it is nearly as bad as any of the other so-called “seven deadly sins,” right?
Perhaps C.S. Lewis can offer some illumination on this subject? Our investigation could lead us to a curious, yet edifying, discovery. Just as it enlightened the author of “Ok Google, Who’s Fatter, Me or C.S. Lewis?”
Like many of us, in his prime C.S. Lewis did not consider himself beset with the problem of gluttony. Historically, people have been more physically active when they are young – at least that was true before “addiction” to screens, keyboards and game controls became endemic.
Even a quarter century ago this trend was being seriously studied, as in “Computer Use and Physical Inactivity in Young Adults: Public Health Perils and Potentials of New Information Technologies,” which appeared in the Annals of Behavioral Medicine.
As the capacities of the new information technologies for delivering targeted, tailored health behavior change programs are developed, the issues for physical activity promotion will become particularly salient.
The emerging paradox is that this new behavior setting for physical activity program delivery is also a setting that strongly promotes long periods of sedentariness.
C.S. Lewis, obviously, lived prior to the ravages of this plague. Yet, he was not immune to the temptations of the Seven Eight Deadly Sins, as identified by the Desert Father Evagrius Ponticus.
As already mentioned, C.S. Lewis did not consider himself particularly vulnerable to gluttony. This is illustrated by a witty (and fascinating) postscript to a letter written to his lifelong friend Arthur Greeves in 1930.
P.S. When I said that your besetting sin was Indolence and mine Pride I was thinking of the old classification of the seven deadly sins: They are Gula (Gluttony), Luxuria (Unchastity), Accidia (Indolence), Ira (Anger), Superbia (Pride), Invidia (Envy), Avaricia (Avarice).
Accidia, which is sometimes called Tristicia (despondence) is the kind of indolence which comes from indifference to the good – the mood in which though it tries to play on us we have no string to respond.
Pride, on the other hand, is the mother of all sins, and the original sin of Lucifer – so you are rather better off than I am. You at your worst are an instrument unstrung: I am an instrument strung but preferring to play itself because it thinks it knows the tune better than the Musician.
GULA – J.A.G.
LUXURIA – J.A.G., C.S.L.
ACCIDIA – J.A.G.
IRA – C.S.L.
SUPERBIA – C.S.L.
INVIDIA – C.S.L.
AVARICIA – (neither, I hope)
Two decades later, C.S. Lewis would make a related observation in a letter to his friend Don Giovanni Calabria. Apologizing for the delay of his correspondence, Lewis wrote:
Nothing else was responsible for it except the perpetual labour of writing and (lest I should seem to exonerate myself too much) a certain Accidia [sloth], an evil disease and, I believe, of the Seven Deadly Sins that one which in me is the strongest – though few believe this of me.
Gluttony is Not Synonymous with Being Overweight
I meet few people who do not wish that they weighed a few pounds less than they do. That would include the elder C.S. Lewis. Listen to his self-description in a letter to a young admirer in 1954.
Self-effacing, as always, he said he was nothing special to behold: “I’m tall, fat, rather bald, red-faced, double-chinned, black-haired, have a deep voice, and wear glasses for reading . . .” (I hope this is not the only dimension of Lewis that I come to resemble more as the years pass by.)
The United Kingdom and Ireland have an historically odd manner of assessing a person’s weight. I suspect there is a bit of intentional obfuscation involved when they use the archaic measurement of “stone” rather than pounds or kilograms.
As Britannica says, “the stone is still commonly used in Britain to designate the weights of people and large animals.” Ironically, babies are not weighed this way, presumably because few of them weigh a full stone – fourteen pounds – at birth.
In the military it was important to remain below your maximum allowable weight. This becomes a problem for a fair number of folks (a dilemma with which I’m personally familiar).
Due to the aforementioned problem with sedentary activities, meeting these height and weight guidelines has become a serious issue for many young recruits.
Still, gluttony is not synonymous with weighing more than is healthy for us. Not so, according to a great column at Intellectual Takeout.
It’s typical to associate gluttony with overconsumption, or, an excess of food or drink. But according to C.S. Lewis, that’s only one form the vice takes. The broader definition of gluttony is any inordinate desire related to food or drink. That includes overconsumption, but it also includes overselectivity regarding the type or quality of food and drink.
Derek Rishmawy discusses this Lewisian distinction as well.
I have to admit that I struggle with gluttony. Yet those who know me probably wouldn’t suspect it. Indeed, I’m tempted to deny it myself because I don’t tend to have a weight issue . . . All the same, this is a sin I’m beginning to realize I need to be increasingly watchful against.
Of course, that confession only makes sense when you understand that there’s more than one way of being a glutton. I’ll let C.S. Lewis explain what I mean.
He cites Screwtape’s letter to his demonic protégé reveling in one of the seldom noticed “victories” of humanity’s Enemy.
One of the great achievements of the last hundred years has been to deaden the human conscience on that subject, so that by now you will hardly find a sermon preached or a conscience troubled about it in the whole length and breadth of Europe.
This has largely been effected by concentrating all our efforts on gluttony of Delicacy, not gluttony of Excess. Your patient’s mother . . . She would be astonished . . . to learn that her whole life is enslaved to this kind of sensuality, which is quite concealed from her by the fact that the quantities involved are small.
But what do quantities matter, provided we can use a human belly and palate to produce querulousness, impatience, uncharitableness, and self-concern? (The Screwtape Letters)
Now, there is something for us to examine in our own lives.
As for those troubled by their physical weight (be it higher or lower than they would like), I discovered an entertaining site where you can find out how much you would weigh on any of the other planets in our solar system.
Exploratorium lifted my spirits by informing me that on Mars I would weigh a mere 96.1 pounds! And best of all, that’s less than seven stone!
The illustration above is based on a detail from The Seven Deadly Sins and the Four Last Things painted c. 1500 by Hieronymus Bosch.